Rigorous and rapid evidence assessment in digital health with the evidence DEFINED framework - npj Digital Medicine
Introduction:
- Digital health (DH) has seen significant growth in recent years.
- Current practices in DH have been described as the "Wild West," with misleading claims and poor clinical evidence quality.
- Digital health interventions (DHIs) are digital technologies aimed at improving health outcomes and behaviors.
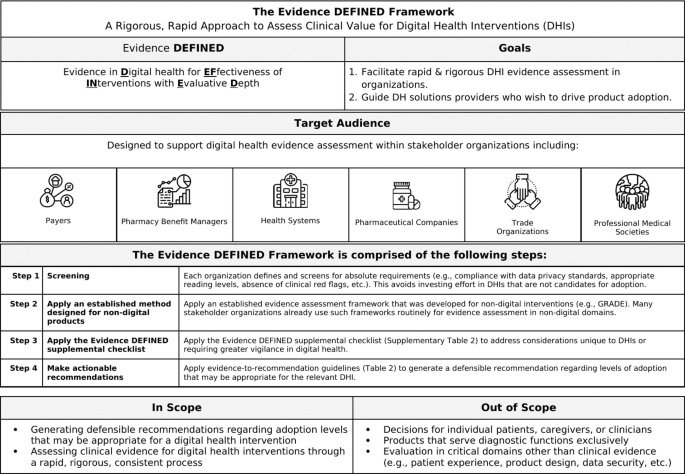
Evidence DEFINED Framework:
- Proposed framework to assess Evidence in Digital health for EFfectiveness of INterventions with Evaluative Depth (Evidence DEFINED).
- Designed for real-world use to streamline DHI assessment.
- Includes a quick start guide and a checklist summarizing high-priority evidence considerations in digital health.
- Introduces evidence-to-recommendation guidelines specifying degrees of adoption based on evidence quality levels.
- Differs from prior frameworks by incorporating unique elements for rigor and speed.
- Rigor is increased by addressing three gaps in prior frameworks related to evidence considerations in digital health, evidence quality criteria in the regulatory context, and leveraging established methodologies.
- Speed is achieved through screening optimization and deprioritization of low-value steps.
Goals of Evidence DEFINED:
- Facilitate standardized, rapid, rigorous DHI evidence assessment in stakeholder organizations.
- Guide digital health solutions providers (DHSPs) in generating evidence that drives DHI adoption.
Need to assess evidence for digital health interventions:
- Urgent need to improve health outcomes and reduce costs for chronic conditions.
- Digital health interventions hold promise, but only equitable, effective, and safe DHIs should be adopted.
- DHI adoption is sometimes driven by marketing rather than evidence.
- Criteria for DHI assessment vary across organizations, and evaluative depth varies.
- Rigorous and standardized evidence assessment methods are needed.
Current evidence assessment frameworks:
- Dozens of frameworks proposed for DHI evidence assessment.
- Many prior frameworks are underdeveloped in the domain of clinical outcomes assessment.
- Prior frameworks often contain superficial questions and minimal evaluation of evidence quality or bias.
- Addressing three gaps in prior frameworks related to evidence quality criteria unique to digital health, regulatory landscape, and leveraging established methodologies.
Inclusion of Evidence DEFINED Framework:
- Evidence DEFINED addresses the gaps in prior frameworks and includes a supplementary checklist of evidence quality criteria for DHI assessment.
- Framework utilizes established evidence assessment methodologies developed for non-digital interventions.
- A comprehensive review of prior frameworks is provided in the article.
Overall, the Evidence DEFINED framework aims to provide a rigorous and rapid assessment of evidence for digital health interventions, addressing the specific needs of stakeholder organizations and guiding the adoption of DHIs that are most likely to improve health outcomes.