
@ShahidNShah

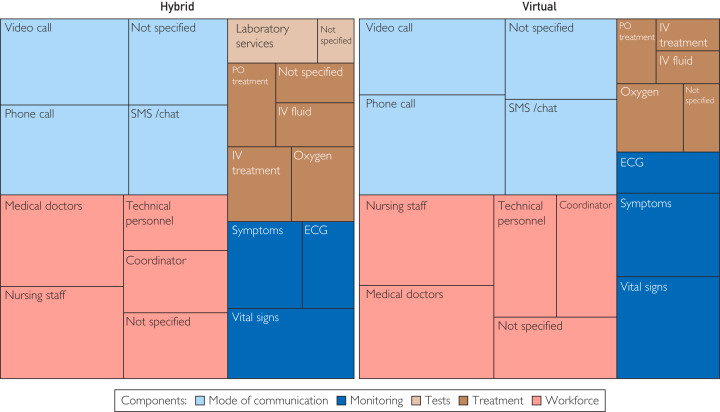
Given the imbalance between high care demand and strained hospital capacity, hospital-at-home (HaH) models offer a potential solution by providing hospital-level care in patients’ homes. This scoping review maps the literature on hospital-led virtual health care within HaH models for acute infections, focusing on intervention characteristics and evaluation designs. Following Johanna Briggs Institute guidelines and PRISMA-ScR, we included studies on virtual and hybrid HaH models using telemedicine for remote monitoring and interventions.
Hospital-at-home (HaH) models that blend virtual care with remote monitoring and telemedicine can help U.S. health systems reduce hospital strain, lower costs, and improve patient satisfaction by delivering acute-level care safely in patients’ homes—especially vital amid workforce shortages and rising care demand.
Continue reading at pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
An increasing number of digital health interventions (DHIs) for remote postoperative monitoring have been developed and evaluated. This systematic review identifies DHIs for postoperative monitoring …
Connecting innovation decision makers to authoritative information, institutions, people and insights.
Medigy accurately delivers healthcare and technology information, news and insight from around the world.
Medigy surfaces the world's best crowdsourced health tech offerings with social interactions and peer reviews.
© 2026 Netspective Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Built on Mar 3, 2026 at 3:59am