
@ShahidNShah

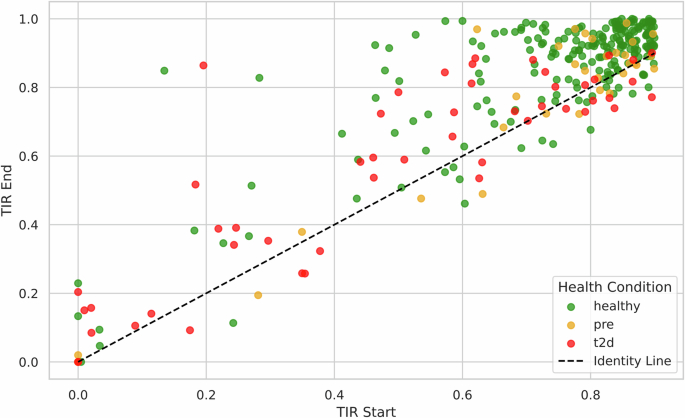
This retrospective cohort study evaluates the impact of an AI-supported continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) mobile app (“January V2”) on glycemic control and weight management in 944 users, including healthy individuals and those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes (T2D). The app, leveraging AI to personalize feedback, tracked users’ food intake, activity, and glucose responses over 14 days. Significant improvements in time in range (TIR) were observed, particularly in users with lower baseline TIR. Healthy users’ TIR increased from 74.7% to 85.5% (p < 0.0001), while T2D users’ TIR improved from 49.7% to 57.4% (p < 0.0004). Higher app engagement correlated with greater TIR improvements. Users also experienced an average weight reduction of 3.3 lbs over 33 days. These findings suggest that AI-enhanced digital health interventions can improve glycemic control and promote weight loss, particularly when users are actively engaged.
The study found significant improvements in TIR among users with lower baseline values (< 90%).Healthy users exhibited an increase from 74.7% to 85.5% (p < 0.0004), whereas users with T2D showed an improvement from 49.7% to 57.4% (p < 0.0004). “Power users” also demonstrated a statistically significant increase in TIR relative to the group as a whole, from 75.5% to 85.6%. This suggests a correlation between engagement and glycemic control.
Continue reading at nature.com
The synergy between AI and telemedicine unlocks countless opportunities to transform healthcare. Among the most significant are two critical advancements: achieving better chronic disease control and …
Connecting innovation decision makers to authoritative information, institutions, people and insights.
Medigy accurately delivers healthcare and technology information, news and insight from around the world.
Medigy surfaces the world's best crowdsourced health tech offerings with social interactions and peer reviews.
© 2026 Netspective Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Built on Mar 10, 2026 at 4:49am